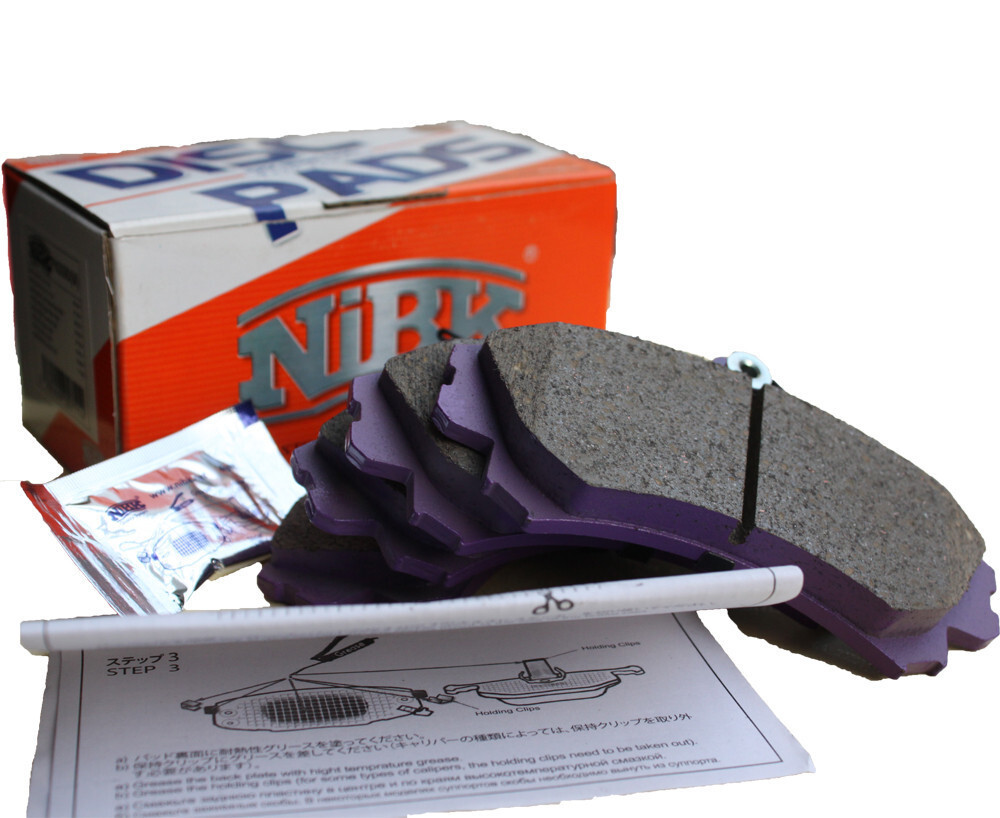
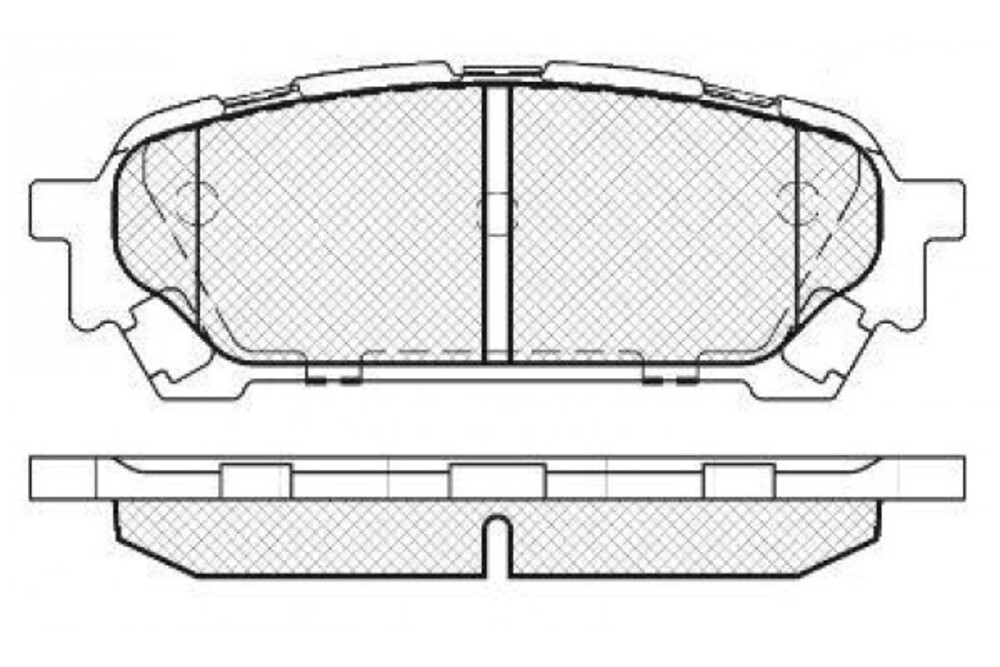
Brake Pads Rear Set. Low Dust. Japan Quality (Equiv to DB1672)
Product Code: PN7801
Price:
Share This Item:
| 01 |

NiBK has been expanding the product range of brake parts for Japanese, Korean, European, American, and other Asian manufactured cars. Setting NiBK’s focus on Japanese vehicles’ brake parts, NiBK has also put in every effort to reach out to more brake parts for vehicles from around the world.
Brakes are one of the most key safety parts of vehicles, and it is essential to ensure that parts like brake pads, shoes, lining, and rotors, are of high reliability and quality.
Stopping is a core function of all vehicles. To ensure the safe driving, the vehicle must be able to stop safely. In order to provide an increasingly safer and more comfortable ride for drivers, NiBK is dedicated to the building up of revolutionary brake products, which will meet the market needs in an appropriate manner, and satisfy our clients’ requirements for competitive and innovative components. Staying connected with our clients is an advantageous entity, and NiBK sees it as a stepping stone for areas of improvement.
NiBK brake pad on rotor
Friction materials are the main components that contribute to braking. Disc brake pads and brake shoes are mainly made up of friction materials. Disc brake pads stop the brake disc rotors, while the brake shoes stop the brake drums, which stop the wheels from rotating. NiBK develops friction materials that deliver excellent braking experience, comfortable, quiet, and powerful. Friction material may vary depending on the type of application, such as passenger cars, performance cars, trucks, and buses.
| Conventional class formulas for all types of automotive and light industry vehicles. (Produced in Purple Now!) | 02 |

Includes a wide range of friction materials marked (at back plate) as J101C, J102E, J103M, J104M, J201C, J202E, J301C, J507E, J508E, J601C, J602C. Different materials are needed to cover an extensive range of applications in automotive and industrial vehicles. Each formula is optimally brewed for its specific purposes in each vehicle class it is used for. The base materials used here are Non Asbestos Organic (NAO), Non abrasive Low Metallic (NALM) and several types of quality Ceramic wools (CEM) with different additives and unique production processes. All the above materials are environmentally friendly - with lowest brake dust levels to protect the environment and keep your rims free of unsightly brake dust. The friction class by LINK dynamic test for all formulations is from “F” to “G”. It guarantees drivers highest road safety with high resistance to FADE (brake power loss in extreme situation). The extensive available range of options ensures comfortable and effective brake filing for each different car and driving style. Ensuring safety and long life of brake rotor.
| Installation Tips | 03 |
Changing the brake pads may be a simple job, but there are few important points that are usually missed or forgotten by installers, which can lead to noise and vibration when you brake, and usually the brake pad quality is to be blamed for it.
It is true that the brake pad is the most crucial component in the braking process, however even the best quality brake pads is not able to “absorb” all vibrations. It may be caused by the conditions of other parts in brake system or even improper installation.
Brakes are critical safety parts for all vehicles. For installation of brakes, we strongly encourage drivers to always approach certified mechanics or maintenance garages when replacing brake parts. After installation, please remember to depress the brake pedal several times from inside the car so as to ensure that the pedal is comfortable for you.
?Note: It is possible that you require several pumps of the brake pedal to allow the brake pads to seat into the new positions.
| Main Components of Brake System | 04 |
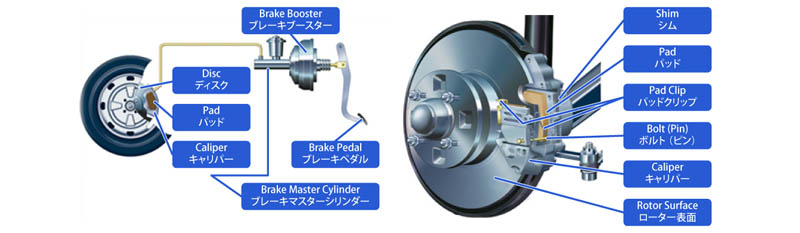
The illustration of the main components of a brake system.
| Preventive Measures of Brake Vibration & Noise | 05 |
Points to take note during installation:
- Condition and Quality of Brake Disc Rotor
If the brake disc rotor surface is uneven or damaged or has a grooves over 0.012? (0.305mm) depth, it needs to be skimmed, or turned by using an on-car lathe, or even taking it to workshop for a new replacement. Usually the inner and outer part of braking surfaces will have grooves left by the old brake pad, especially if the friction material contains a high level of steel fibre that is used by many manufacturers for production simplicity and cost-saving. This is often hard to be overlooked, as this may result in the new set of brake pads to have no proper contact with the rotor surface, which will lead to noise, vibration and fast wear off of friction material.
If the brake disc rotor is in a good condition, it also important to sand the rotor surfaces on both sides lightly, with a piece of 100-grit sandpaper so as to smooth the surface. An orbital sander works well for this job, since it gives the rotor a non-directional finish, which is recommended by most car manufacturers. Sanding the rotor surfaces will remove any residue or brake pad adhesive that was deposited by the old brake pads. This prevents the possibility of noise and vibration when the new set of brake pads is installed. - Lubricating on Contact Surfaces
It is advisable to lubricate the following contact surfaces:- Caliper bolts (pins)
- Clips, shims and anchors where it touches the brake pads and calipers.
- Back plate of brake pads (on both edges) and in the centre where cylinders push.
- Rotor mounting place where brake disc rotor fixed on bearing hub and axel.
(It is especially important if the rotor was replaced.)
High temperature grease, like Molycote77, should be used and ensure that the lubricant will not contaminate the friction material and rotor braking surface. - All shims, anchors and clips should be present and have “like new” condition
If the conditions of the shims are bad, or it is misplaced and you are unable to replace it by new one, then a thin layer of high temperature silicone could be used as the last resort.
If caliper uses anchor brackets to fit brake pad, make sure it has not been worn out. The brake pad should fit very snug in the anchor bracket. - Caliper slides (where brake pads load), bushings, bolts (pins) must be clean and rust free
It is also very important to make sure that the wheel flange behind the rotor is free of any rust or debris. Failure to eliminate rust or debris will cause rotor “run out,” which, over time, will cause friction material to be transferred to the rotor surface. This might eventually cause noise due to extreme variance in rotor thickness. - Caliper bolts must not be bent and must be torque to manufacturer spec
Otherwise, it may cause the brake pads to be not on the proper position on the brake disc rotor, resulting in brake jam, noise, vibration, etc.
| Bedding-In of Brake Pads | 06 |
You shouldn’t rely on the first impression to evaluate the quality of the brake pads. For optimum performance, you should allow some time for the brake pads and brake disc rotors to be properly bedded-in. This is also known as burnishing or break-in. In other words, to allow the brake pads to bed-in means to create an even layer of the friction material on the brake pads on the rubbing surface of the brake disc rotor. Bedding-in procedures may differ for various brake systems, friction materials, and driving conditions, hence, it may not be easy determine the time and distance required for the brake pads to be properly bedded-in.
| Overheated Brake Pads | 07 |
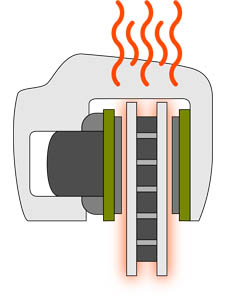
If your brake pads are overheated (more than 450°C) for long period of time due to reasons like unnatural racing driving, caliper mechanical problems, driving with hand brake, then it is highly possible that performance of your brake pads will be downgraded. The braking power will be reduced. It caused by burning of heat sensitive components in the friction material.
| Life of Brake Pads | 08 |
When the friction material of the brake pad has been worn out, remaining with less than 5mm thickness of the brake pad, the temperature of the friction material can easily increase, causing the brake pad to wear off even quickly. Thus, it is strongly recommended to replace the brake pads at the thickness of 5mm.
| 09 |

Brake pads with thickness of 10mm or more are at a safe state for usage
| 10 |

Brake pads with thickness of 5mm or less are not advisable for usage. Brake pads should be replaced as soon as possible
| 11 |
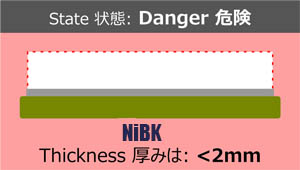
Brake pads with thickness of 2mm or less are strongly not advisable for usage as it is extremely dangerous. Brake pads should be replaced immediately.
| Disc Brake Pads | 12 |
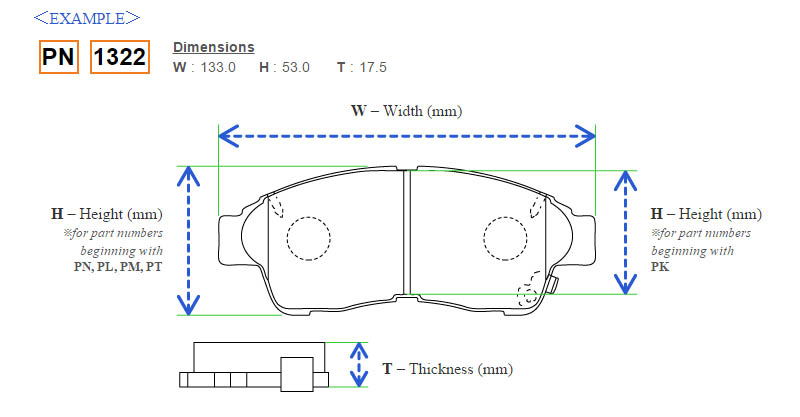
| Product Type | Brake Pads |
| Length | 108.5 mm |
| Packing Weight | 1660 g |
| Width | 39 mm |
| Thickness | 14 mm |
| Kit | 4 Pcs |
| Packing Width | 42 mm |
| Packing Depth | 110 mm |
| Packing Height | 60 mm |
| Fitting | Rear-Axle |
| Package Type | BOX |
Be The First To Review This Product!
Help other Aurus Australia Pty Ltd users shop smarter by writing reviews for products you have purchased.